A smart card, chip card, or integrated circuit card (ICC) is any pocket-sized card with embedded integrated circuits. Smart cards are made of plastic, generally polyvinyl chloride, but sometimes polyethylene terephthalate based polyesters, acrylonitrile butadiene styrene or polycarbonate. Smart cards can provide identity documentation, authentication, data storage, and application processing. Smart cards may provide strong security authentication for single sign-on (SSO) within large organizations.
Subscriber identity module or subscriber identification module (SIM) is part of the function of a Universal Integrated Circuit Card (UICC) physical smart card, which is usually made of PVC with embedded contacts and semiconductors.
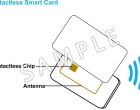
Contactless smart card, the card communicates with and is powered by the reader through RF induction technology (at data rates of 106–848 kbit/s). These cards require only proximity to an antenna to communicate. Like smart cards with contacts, contactless cards do not have an internal power source. Instead, they use an inductor to capture some of the incident radio-frequency interrogation signal, rectify it, and use it to power the card’s electronics.